
As with the evolution of networking technology, it is difficult for older ethernet cords to keep up with modern technologies. Therefore, the Ethernet cable is developed to be able to transmit the speed with the required quality.
What is an ethernet cable?
An Ethernet cable is the cable that connects your computer to the Internet. An Ethernet cable, a type of network cable, is a wire that runs from a router, modem, or network switch to your computer, allowing your computer to access the local area network (LAN).
Benefits of an ethernet cable
- Faster and more consistent Internet connection because no objects are blocking Wi-Fi signals, for example.
- It does not cause a sudden drop in internet speed.
- Stable lag while playing video games with an ethernet cable means less lag and faster loading times for games.
- Every device can be connected to an Ethernet port - however, Ethernet cables are designed to snap in place, so they're hard to pull out accidentally.
Ethernet cables come in various lengths and colors, and both sides of the wire are the same, no matter what cable or device you use to connect the wires.
What are the types of Ethernet wires?
1- Cat 1
Cat 1 cable is an abbreviation for (Category 1) and since 1974 AD, Xerox PARC began developing the first Ethernet wire and defines a traditional UTP cable, and it was the first launched for general use in the year 1980 AD. It is designed to transmit only voice, not data. This type of cable is not recommended for networking purposes and is used in telephony services.
2- Cat 2
In 1982, a cable was developed that could transfer data up to 4 megabits per second. Consists of 4 pairs of wires.
3- Cat 3
After the establishment of the IEEE organization, Ethernet wire was developed starting in the mid-1990s and can transmit data at up to 10 Mbps. Consists of 4 pairs of wires. It is 300m long with markings every 0.6m. The frequency of this cable is 16MHz and is used for the 10BaseT network.
4- Cat 4
TIA/EIA does not recognize this cable and can transmit data up to 16 Mbps. The cable consists of 4 pairs of wires. The signaling frequency of this cable is up to 20MHz.
5- Cat 5
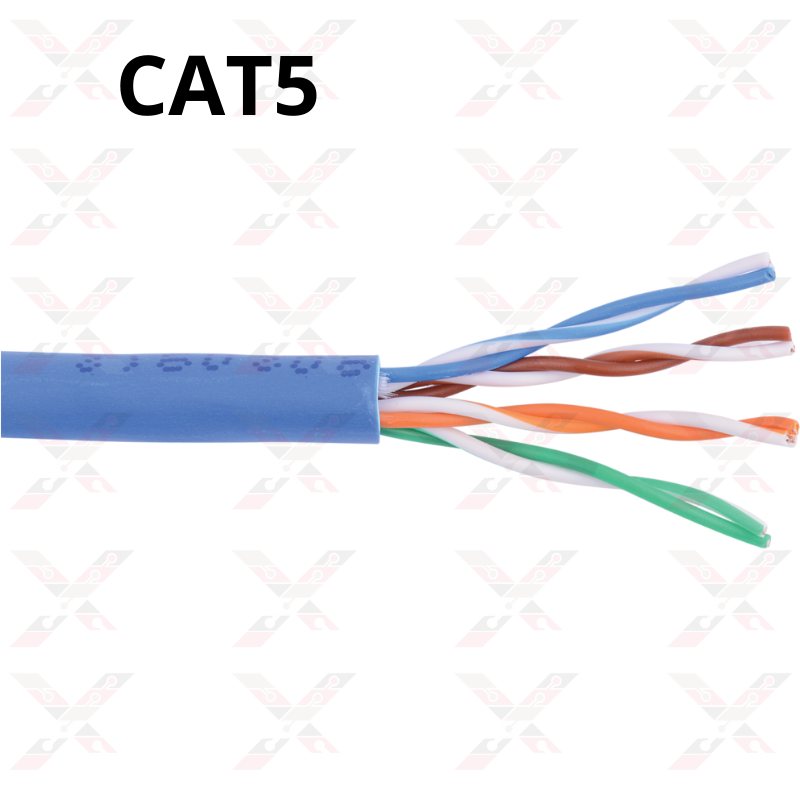

Fiber optic Ethernet was developed and first used in data centers in 1994. This is the most widely used network cable for 100Base-T and 1000Base-T networks because it provides performance allowing data at 100 Mbps and slightly more (125 MHz for 1000Base-T) Ethernet. Cat 5 cable replaced Cat 3 and became the standard for Ethernet cabling for several years. Cat 5 cable is obsolete and therefore not recommended for existing new installations. Cat 5e or Cat 6 is now used for all modern structured cabling installations. Many large organizations have policies that state that any upgrade to a Cat 3 network must include an upgrade to Cat 5e.

Cat 5 cables are the oldest type of Ethernet cable since their introduction in 2001, which was designed to support theoretical speeds between 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps. However, gigabit speeds can still be achieved with Cat 5 cable especially if the cable is shorter, but it is not always a guarantee. It supports bandwidths of up to 100 MHz. The "e" in Cat 5e stands for "improved" and as the name suggests, it's a fundamental improvement over Cat 5 cables. In theory, it should be up to 10 times faster than Cat 5 cables without a significant price increase. It supports up to 1000 Mbps or gigabit speeds. Cat 5e cables have lower crosstalk marks and provide faster, more reliable, and consistent speeds than Cat 5 cables.
6- Cat 6
Developed in 2002, Cat6 is a 4-pair cable that provides improved performance over Cat 5e. It can carry data up to 1000 Mbps at a signal frequency of 250MHz.

Cat6 cables and Cat6a cables introduced in 2008 are among the most popular types of Ethernet wire. They have more specs than Cat 5e cables and can support 10Gbps. They have thicker wires, and the cores are more tightly together. This means that the cables are thicker and less flexible than Cat 5e cables. Cat 6 cables are recommended for large organizations that handle large files. For home purposes, Cat 5 and Cat 5e are positive enough.

Cat 6a cables have enhanced properties and can operate at 500MHz and can support 10Gbps over a maximum distance of 100m.
Cat6a has better protection than Cat6 cables.
7- Cat 7
Cat7 cable is defined as a fully shielded twisted pair that can transmit data up to 10000 Mbps or 10 GB and operates at a signal frequency of 600 MHz. Full protection means that all four pairs of cables have an additional shield over them.
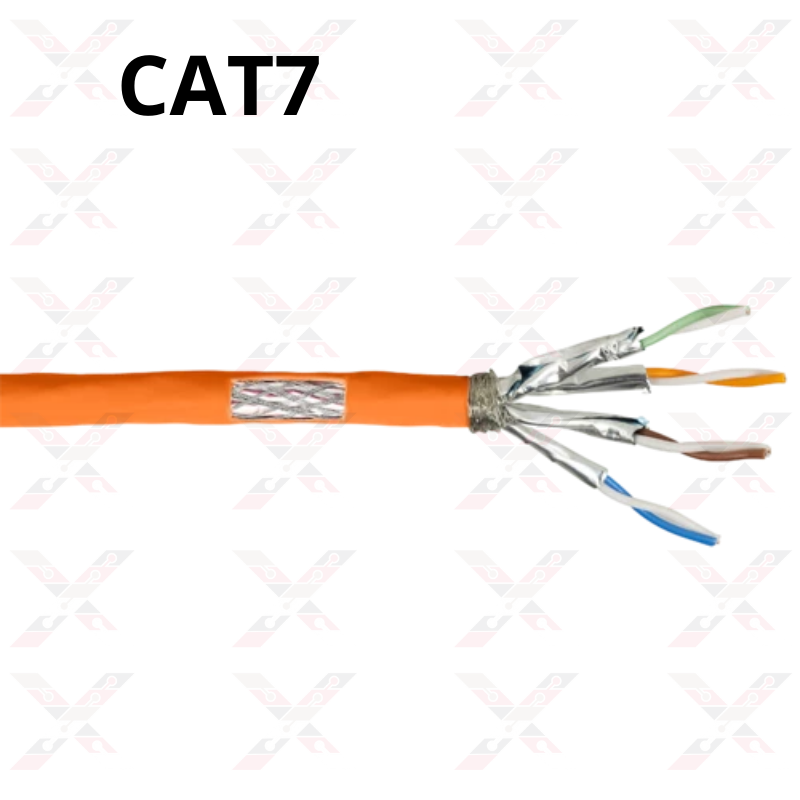

Cat 7 cabling has more specifications compared to Cat 6. Shielding has been added to individual wire pairs on Cat 7 Ethernet wire. It is designed for Gigabit Ethernet over 100 meters of copper cabling and is rated for transmission frequencies up to 600MHz. Cat 7a cables operate at frequencies up to 1000MHz. It is designed for multiple applications in one cable including 40G, 100G, and CATV. The conveying distance can be up to 50m for 40g and 15m for 100g.
Cat7 also known as Category F cable consists of covered twisted pairs (SSTP) of wires. It is more insulated and thicker and bulkier than Cat6e cable. It's a little hard to bend but it achieves data transfer speeds of 10,000 Mbps over its 600 MHz bandwidth.
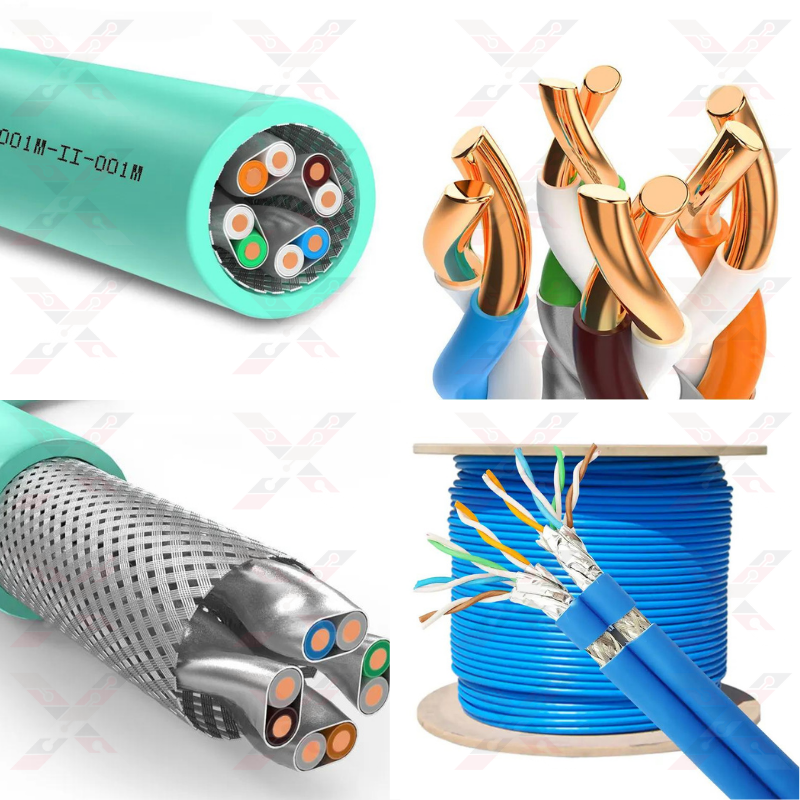
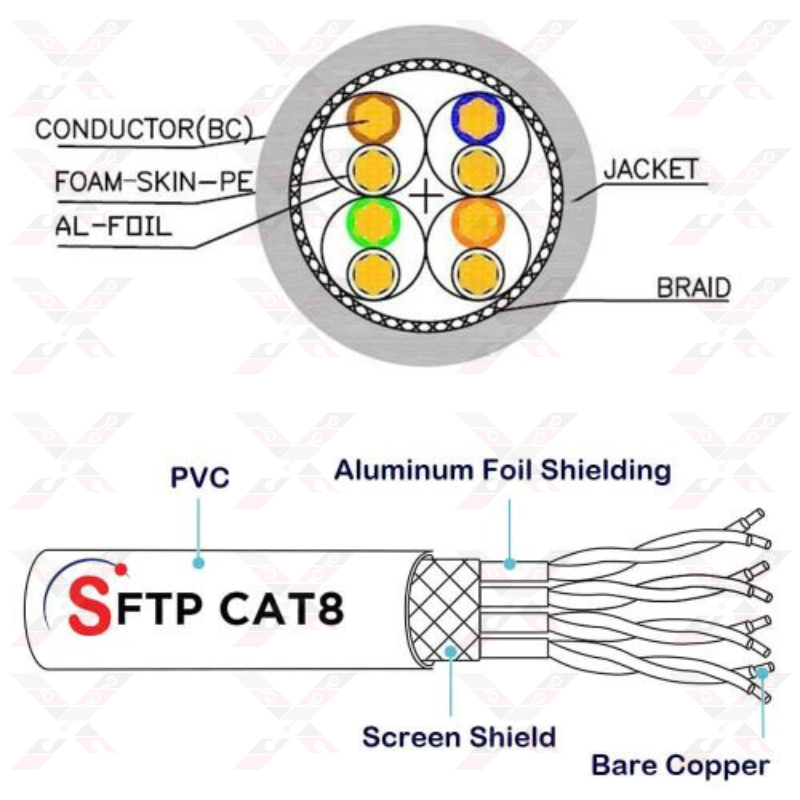
8- Cat 8
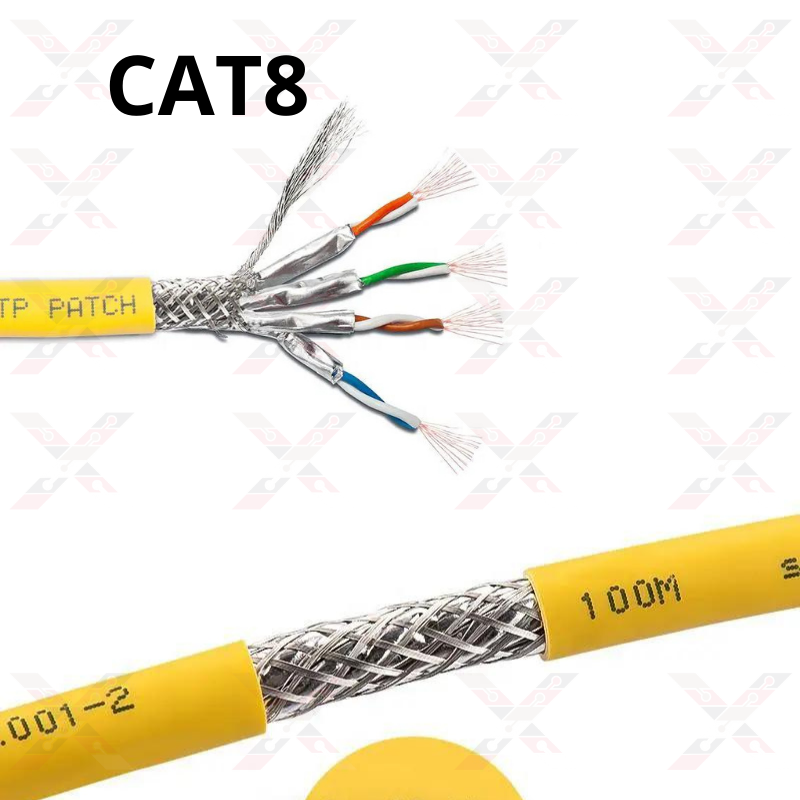

In 2016, Cat8 was developed, which is the latest network cable. Cat8 operates at frequencies up to 1000MHz to transfer data from 25Gbps to 40Gbps. This new technology features one of the largest ever Ethernet speed increases with a data rate of 40Gbps and a bandwidth of 2000MHz. It's a serious upgrade, and the implications are eye-catching across the IT domains.
Features of Cat8 Ethernet Wire

- Best of all, these cables come at an affordable price, providing a lower-cost alternative to fiber.
- Cat8 cable is capable of achieving higher speeds due to the shielding that has been implemented in the design.
- Each pair of conductors is shielded with aluminum foil to reduce and eliminate interference.
- Cat8 ethernet cables are used with 26 AWG copper conductors to give the best signal available with a high level of flexibility, making it easy to install in tight spaces.
- Cat8 cable provides improved Power over Ethernet (PoE) performance. It can handle higher levels of Power over Ethernet (PoE) output due to its lower DC impedance.

