
What is an HDMI cable and what are its uses? What are its types and supported technologies for each kind? How do I choose the right HDMI cord for my needs?
In light of the rapid technical development, especially in the field of audio and video, many users find it difficult to choose the appropriate devices for their needs.
In this article, I'm going to explain everything you need to choose the suitable HDMI cable for your needs.
HDMI Cables Types:
As with the development of audio and video technologies, it is difficult for older HDMI cables to keep up with modern technologies. Therefore, HDMI wires are being developed to be able to transmit audio and video with the required quality.
HDMI cables vary in bandwidth, resolution, and the formats they support.
There are several HDMI® cable types plus a special cable certification designation to choose from; each designed to meet a particular performance standard. Here is an overview of the HDMI cable types, their capabilities, and how to tell them apart.
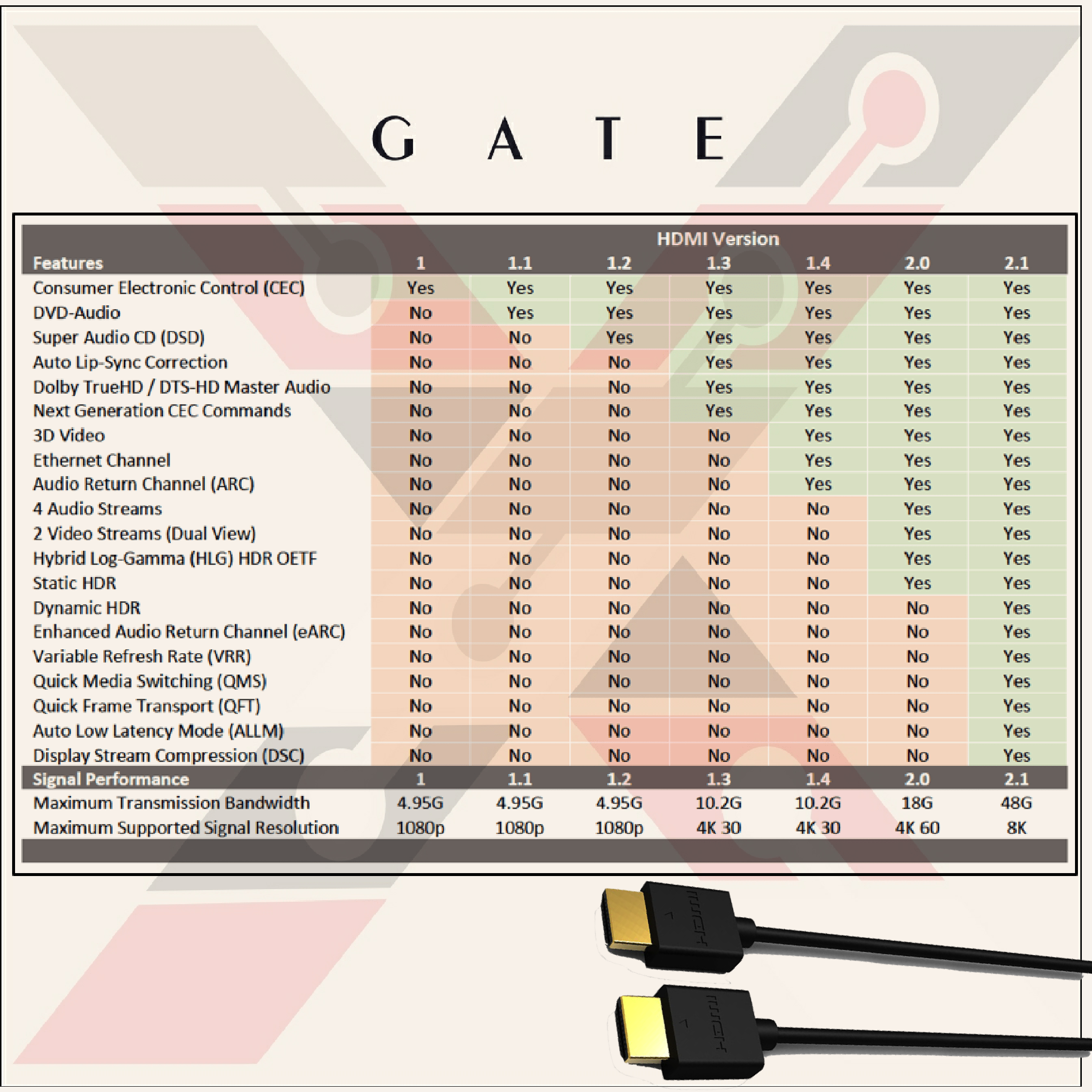
According to the HDMI.org classification, HDMI cables are divided into four types:
- HDMI 1.3 القياسي (Standard HDMI)
- HDMI 1.4 عالي السرعة (High-Speed HDMI)
- HDMI 2.0 بريميم عالي السرعة (Premium High-Speed HDMI)
- HDMI 2.1 فائق السرعة (Ultra High-Speed HDMI)
1- HDMI القياسي (Standard HDMI)
Version 1.0 was launched at the end of 2002.
It was upgraded to version 1.3 in mid-2006.
Speed: 4.95Gbps
Resolution: 720i or 1080p
The standard HDMI cable does not support 4K resolution, so it is not recommended to purchase it unless your TV does not support 4K
2- HDMI عالي السرعة (High-Speed HDMI)
Version 1.4 was launched in mid-2009.
Speed: 10.2Gbps
Resolution: 1080p120fps, 4K@30fps
High-Speed HDMI cable supports resolutions up to 4K at 30fps. It can also deal with 3D content and various technologies such as ARC and HDR10. Still, this version does not support other HDR formats (Dolby Vision or HDR10 +), so it is the most appropriate option when your TV does not support advanced HDR formats.
3- HDMI بريميم عالي السرعة (Premium High-Speed HDMI)
Version 2.0 was launched in the late third quarter of 2013.
Speed: 18Gbps
Resolution: 1080p@240fps, 4K@60fps
This cable supports resolutions up to 4K at 60fps. It can also play 8K content at 30 frames per second. This version supports HDR formats (HDR10, HDR10+ HLG, and Dolby Vision), which makes it the perfect choice for video game consoles and TV broadcasters that support these technologies.
This type of wire is considered the most suitable in 2020 for most, as it supports resolutions up to 4k, which makes you do not need a higher version unless your TV screen supports 8K quality.
4- HDMI فائق السرعة (Ultra High-Speed HDMI)
Version 2.1 started in the late fourth quarter of 2017
Speed: 48Gbps
Resolution: 8K@60fps, 4K@120fps
Ultra High-Speed HDMI cable is the latest technology in the industry as it can handle resolutions up to 10K at 30fps, 8K at 120fps uncompressed, or 4K at 144fps.
The advantages of version 2.1 of HDMI cables over previous versions are:
- It features reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI) as it reduces interference with other nearby wireless devices.
- Supports all advanced features included in previous versions.
- Supports eARC to provide the most advanced audio formats for sound quality (DTS:X and Dolby Atmos).
- Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) technology is an important feature for gaming and multimedia as it reduces lag, jitter, and frame drop for smoother gameplay.
- Quick Media Switching (QMS) technology seamlessly switches between sources between video media and video games without showing a black screen The idea is to reduce potential lags and dropouts when switching between media with different resolutions or refresh rates.
- QFT fast frame transfer reduces lag for smoother, lag-free gameplay and an excellent interactive VR experience.
- ALLM (Auto Low Latency Mode) Allows a video game hardware, PC, or another device to send a signal to the monitor and then automatically switch it to a low-latency, low-lag gaming mode However, a low latency setting may not be ideal for other media types as some processing features on the TV may be turned off to reduce latency. When the ALLM mode is activated, for example, when switching from video games to watching movies, the source deactivates the signal and the screen returns to the previous mode for the perfect picture. (This can work for other uses like karaoke and video calling.)

